|
|
|||||

|
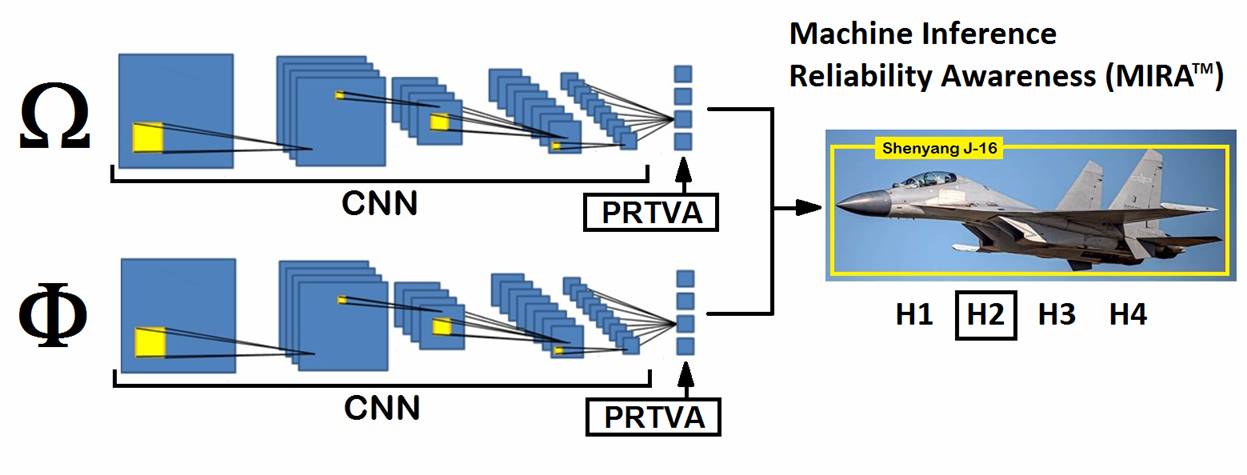
Machine Inference Reliability
Awareness (MIRA™) is a specification for the design of pattern recognition algorithms
and, more generally, of analytical AI algorithms, which has the objective of
making the inferential engine aware of the reliability of the inferences it
generates. The inference engine must communicate the reliability associated
with each inference process. The concept of reliability of the
inferential process should not be confused with the strength of the inference
of a soft label. The latter represents the weight that the inferential
process has given to the specific classification. The reliability is
intrinsic to the methodology used to generate the inference. In pattern recognition algorithms and
neural networks, reliability is often related to the metric used to calculate
vector distances. Some metrics guarantee better generalization performance
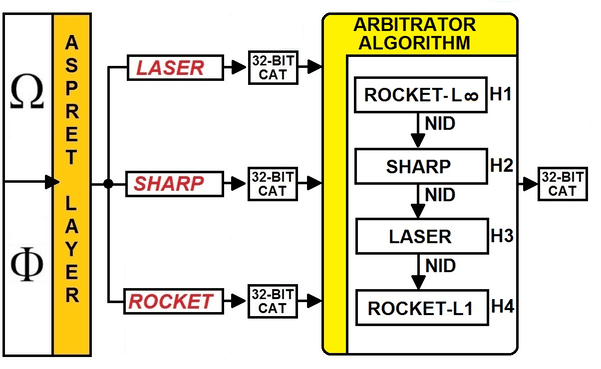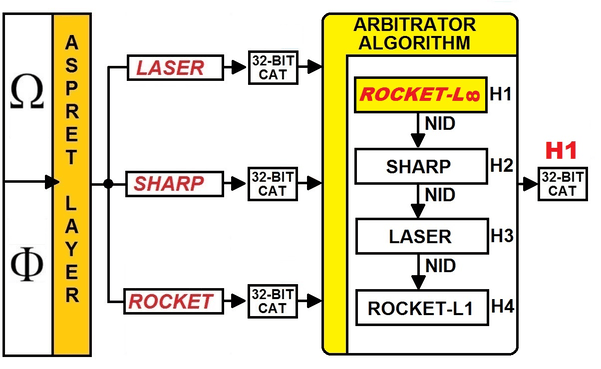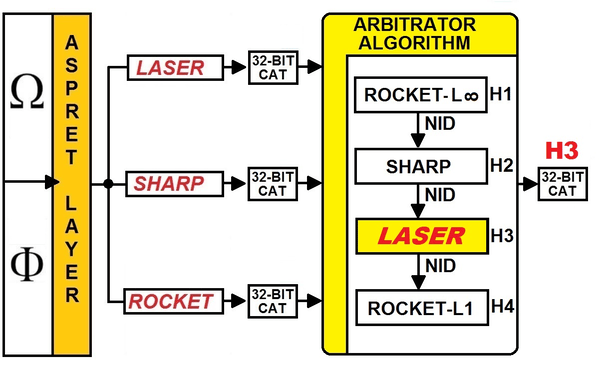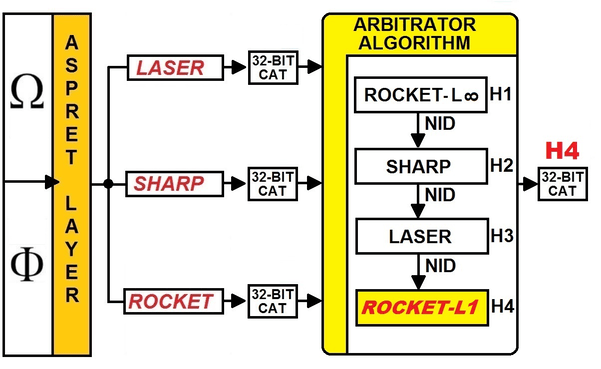
than others but, typically, they are less reliable. PRTVA™ (Pattern Recognition Triple
Version Algorithm™) is one of the technologies developed to meet the
requirements of the MIRA™ guideline. The algorithms can be different and the
metrics can also be different. The number of reliability levels can vary from
2 to N. The common methodology for all implementations of inferential engines
satisfying the MIRA™ requirements is to generate the inference with different
algorithms whose reliability is known: an agent external to the algorithms
must select the result of the inference produced by the algorithm with the
highest reliability. Measuring the reliability of an
inferential process is extremely relevant in any safety critical context and
where the result can be deceived by external agents. PRTVA™ uses three different algorithms
and four distance vector metrics. The PRTVA™ technique implements an
inference engine with four levels of reliability. |

|
|


|
©2024_Luca_Marchese_All_Rights_Reserved Aerospace_&_Defence_Machine_Learning_Company VAT:_IT0267070992 NATO_CAGE_CODE:_AK845 Email:_luca.marchese@synaptics.org |
|
Contacts_and_Social_Media |